How Is The Arctic Ice Changing?
The Arctic has been changing over the years and we have proof of that because of how the amount of sea ice has decreased, how the spring is warming up in Alaska, the warmer winter in Europe, and how lots of ice and snow has turned into swamps and marshes in Alaska. What is happening is global warming. Global Warming is the effect of the increase of man-made greenhouse gases. Greenhouse gases are anything that absorbs infra-red in the atmosphere, like water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, etc. Greenhouse gases make the Earth warmer. Last week, the Arctic ice reached an all time low, that was about 2 million square miles. The Arctic is changing, but some people belive that the Arctic is the only place changing. That is not true. All over the world things are happening. The ice in the Antarctic is getting thicker, summers in certain places might be warmer or even colder. Yes, the Earth is changing, we must accept that, but all this was going to happen eventually. As humans, we are probably speeding up the process, but we cannot just blame ourselves for the happenings all over the world. The Earth is changing.
"Arctic Haze"
Around 1950, a thin haze became noticable in the before clear arctic skyes. This was appearing in northern Alaska and in Western Canada in late winter early spring. The phenomenon increased and became spread out and is now clalled "arctic haze." The haze is much more frequent and appearing all around the Arctic Circle.
The Layers of the Arctic Ocean's Water
The very bottom layer of the Arctic Ocean's water is the densest, saltiest, water. This is because water that is very salty sinks to the bottom of the ocean. The second layer of water is the denser, saltier, water. This is the second layer because it is sort of salty so it does not fully sink. The third and top layer is the least salty, and least dense, so it is the very top layer of water. The Arctic Ocean's layers are very large part of the Arctic.
Beaufort Gyre
The Beaufort Gyre is a clockwise, circular surface Arctic Ocean current and is one of the Arctic's main currents. It turns the Polar Ice Caps and makes 1 full rotation every four years. Gyre is a circular current in a basin. There are only five major gyre's and the Beaufort Gyre is one of the five. In the 1990's some of the ice began to melt before it finished its four-year rotation. The Beaufort Gyre is a major Arctic Current.
Labrador Current
The Labrador Current has an average speed of .3 to .5 miles per hour. The current is a continuation of the Baffin Island Current and Flows southeastward from Hudson Strait (60°N) along the continental slope to the Tail of the Grand Banks (43°N). Hayes and Robe discovered that the Labrador Current might actually be 30% stronger than early estimates. The Current is a cold water current.
East Greenland Current
The East Greenland Current flows from the Fram Strait to Cape Farewell. It transports 90% of the ice leaving the Arctic Ocean. The East Greenland Current (EGC) is a cold water current and has a low salinity, causing it to have a low density. The EGC is a long current and a very important one in the Arctic Ocean.
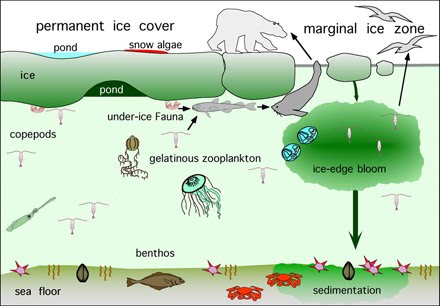
Living things in the Arctic Region
Believe it or not, the Arctic holds about 400 species of plants and flowers. In total, the area has a little over 1,000 living species. Another animal that lives in the Arctic region is the arctic fox. Surprisingly, the arctic fox has the warmest fur of any animal, even warmer than the arctic wolf and a polar bear. Some may confuse where the polar bears live; they live mostly on the ice. They are also the largest land meat eater and the biggest in the bear family. A snowy owl is one of the select birds that live in the arctic year round. As a snowy owl, you would have great vision and can even hunt in the day. This is different from owls that are were we live because they only hunt at night; in the Arctic, you must be able to hunt in the day because some days are completly light. The Arctic is full of animals and plants that must adapt to the cold weather.
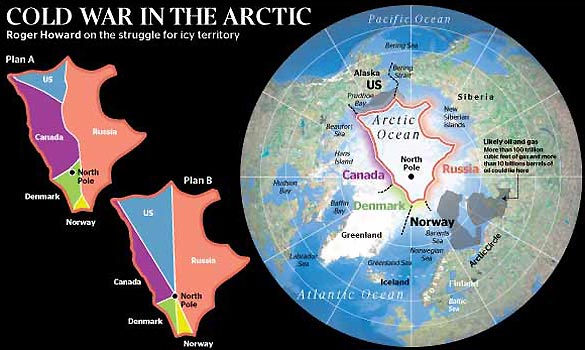
The Cold War
Many countries in the Arctic are trying to claim a piece of the Arctic because they have discovered that the Arctic has 13% of world's undiscovered oil and 30% of the world's undiscovered gases. Below there is a picture of what countries right now have a piece of the Arctic. Russia has the biggest piece of the Arctic Ocean because a lot of it borders part of the ocean. Canada has the second largest piece of the ocean because Canada has the second largest piece of it bordering the ocean. The United States has a very small piece because Alaska borders the Arctic Ocean but Alaska is very small and only a little bit of it borders the ocean. The two smallest pieces are Denmark and Norway. The cold war is still heating up and will become bigger very soon.
Weather in the Arctic Region
The Arctic Recieves nearly 8'' of rain per year. The Arctic is a cold dessert and the growing season lasts only 50-60 days per year. The Arctic Tundara is known to be the world's youngest biome, at 10,000 years old. The average temperture in the Arctic is 15 to -30 dergrees Farenheight. Although the winter might be extreamly chilly, the summer can rise up to 50 dergrees Farenheight.
Place and Location
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest of all the oceans and is nearly 8% of the Pacific Ocean. The Arctic Ocean almost fits completely into the Arctic Circle it is so small! The exact location of the Arctic is 66 degrees and 33 minutes latitude. Did you know that the North Pole is actually in the middle of the Arctic Ocean and that the ocean is about 1.5 times the size of the US?! The area of the ocean is 5,440,000 square miles and a depth of 3, 658 meters.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)